Taylor-Made Prosperity Analyzing How the 'Eras' Tour Impacted the Mexican Economy
By: Anna Su and Abigail Thorne

THE OPENING ACT
In the world of music, few artists can claim the international stardom and adoration commanded by Taylor Swift. In March 2023, Swift embarked on her record breaking “The Eras Tour” in the United States. The market-research firm QuestionPro estimated the economic impact of Taylor Swift's "The Eras Tour" at $5 billion for the US economy. But Swift is only getting started. Beginning the international leg of her tour this past August in Mexico City, "The Eras Tour” is sure to continue breaking records and economists everywhere will be eager to analyze its global economic impact. We predict to see a similar economic impact on the countries where she brings her chart-topping hits and breathtaking performances next, which leads us to our own research question...

What will be the economic impact of Taylor Swift's "The Eras Tour" on the Mexican economy?

This question resonates with both music enthusiasts and economists alike, as it sheds light on the profound interplay between art and economics. "The Eras Tour" has ventured across the US, drawing in millions of fans and generating substantial revenue. It's important to understand how this musical phenomenon shapes Mexico's economic dynamics, from ticket sales and merchandise to hospitality and tourism.
Before we begin, we want to give some background on Taylor Swift...
Taylor Swift, born on December 13, 1989, in Reading, Pennsylvania, has emerged as a highly influential and versatile figure in the music industry. Beginning her career in country music, Swift quickly rose to fame with her self-titled debut album in 2006 and achieved breakthrough success with "Fearless" in 2008. Over the years, she transitioned seamlessly into pop with albums like "Red" (2012) and "1989" (2014), winning numerous awards and establishing herself as a pop icon. Notable for her ability to evolve and reinvent herself, Swift explored themes of fame and perception in "Reputation" (2017) and returned to a romantic pop sound with "Lover" (2019).

Swift's significance extends beyond her musical prowess, with her tours becoming iconic in the industry. The "Fearless Tour" (2009-2010) marked her first headlining venture, followed by the "Speak Now World Tour" (2011-2012), emphasizing her growth as a songwriter and performer. The "Red Tour" (2013-2014) showcased a shift to pop, while the "1989 World Tour" (2015) solidified her as a global pop sensation. The "Reputation Stadium Tour" (2018) and its theatrical elements preceded "The Eras Tour" in 2023, a record-breaking international venture that grossed over $2.2 billion in the United States alone, reaffirming Taylor Swift's status as a music industry titan.
Back to our research...
Our methodology involves correlating regional engagement data with the number of tickets sold for each concert, enabling the execution of a regression analysis. This regression will play a pivotal role in predicting the demand for Mexico City and future concerts on the tour. Subsequently, we plan to conduct a regression correlating this demand with the local unemployment rate. This dual-step analysis aims to unveil the relationship between concert attendance and its consequential impact on the local economy. Ultimately, this predictive modeling approach will empower us to anticipate the potential economic impact of the concert on future tour locations.
We plan to employ Ordinary Least Squares (OLS) regression analyses to explore on specific relationship: the association between relative regional engagement and the unemployment rate. This regression analysis will play a pivotal role in quantifying and illuminating the interconnections among these variables, offering valuable insights into the influence of regional engagement on local unemployment rates.
We aim to produce one primary output: a graphical representation illustrating the relationship between regional engagement and the unemployment rate. This graph will incorporate Ordinary Least Squares (OLS) regression lines, enabling us to leverage the model for predicting the potential economic impact on the Mexican economy. The visualization will serve as a valuable tool in understanding and forecasting the intricate connection between regional engagement and the local economy.
__________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
DIRECTED ACYCLICAL GRAPH
Our objective is to address this question through a comprehensive analysis leveraging multiple data sources. This approach entails accessing concert revenue reports, tourism statistics, and examining the broader ripple effects on various industries. The analysis will incorporate economic modeling techniques and the construction of a Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG). This DAG will serve as a visual representation to illustrate the intricate relationships between variables, providing insights into how Taylor Swift's tour may impact the Mexican economy from various perspectives.
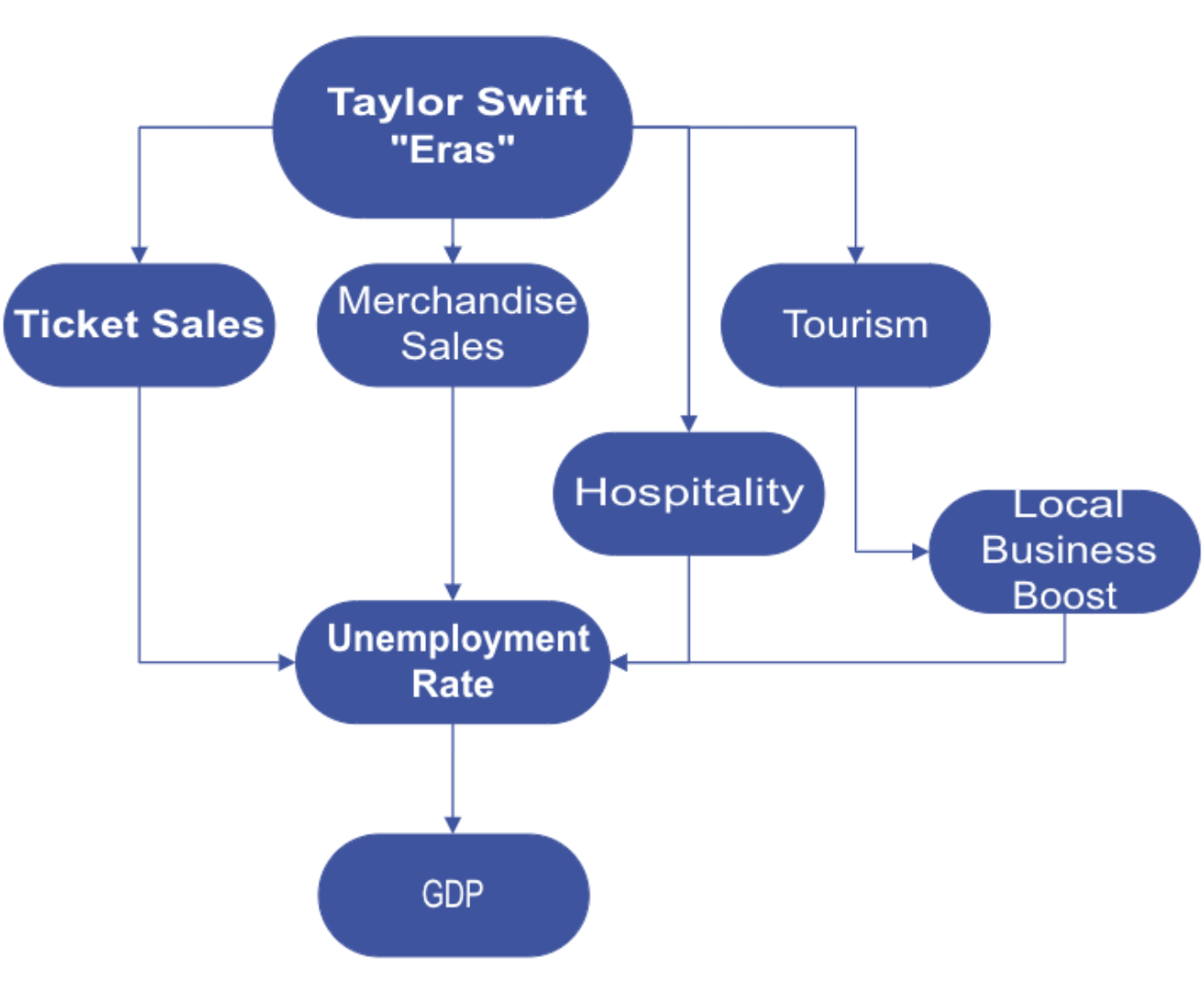
The Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG) crafted at the project's inception serves as our foundational framework, tracing the intricate relationships between various facets influenced by Taylor Swift's "The Eras Tour." The tour initiates a cascade effect, impacting critical elements such as ticket sales, merchandise sales, hospitality, and tourism. Specifically, the tourism component contributes to a localized boost in business, creating a ripple effect on the broader economic landscape. These interconnected factors, in turn, play a role in shaping the unemployment rate—a pivotal indicator with repercussions on the overall Gross Domestic Product (GDP). The DAG serves as a visual narrative, illuminating the interconnected web of influences stemming from the tour and its profound implications on both micro and macroeconomic dynamics.
Regrettably, due to the recent nature of Taylor Swift's "The Eras Tour," comprehensive and verified data from reputable sources has yet to be made available. In light of this limitation, our analytical approach took a deliberate shift towards alternative methodologies and data sources. This adaptive strategy enabled us to navigate the absence of conventional datasets, ensuring that our analysis remains robust and insightful despite the inherent challenges posed by the unavailability of recent, authoritative information. By embracing a different path, we aimed to extract valuable insights and contribute to a nuanced understanding of the economic impact of the tour, even in the absence of the customary wealth of data.
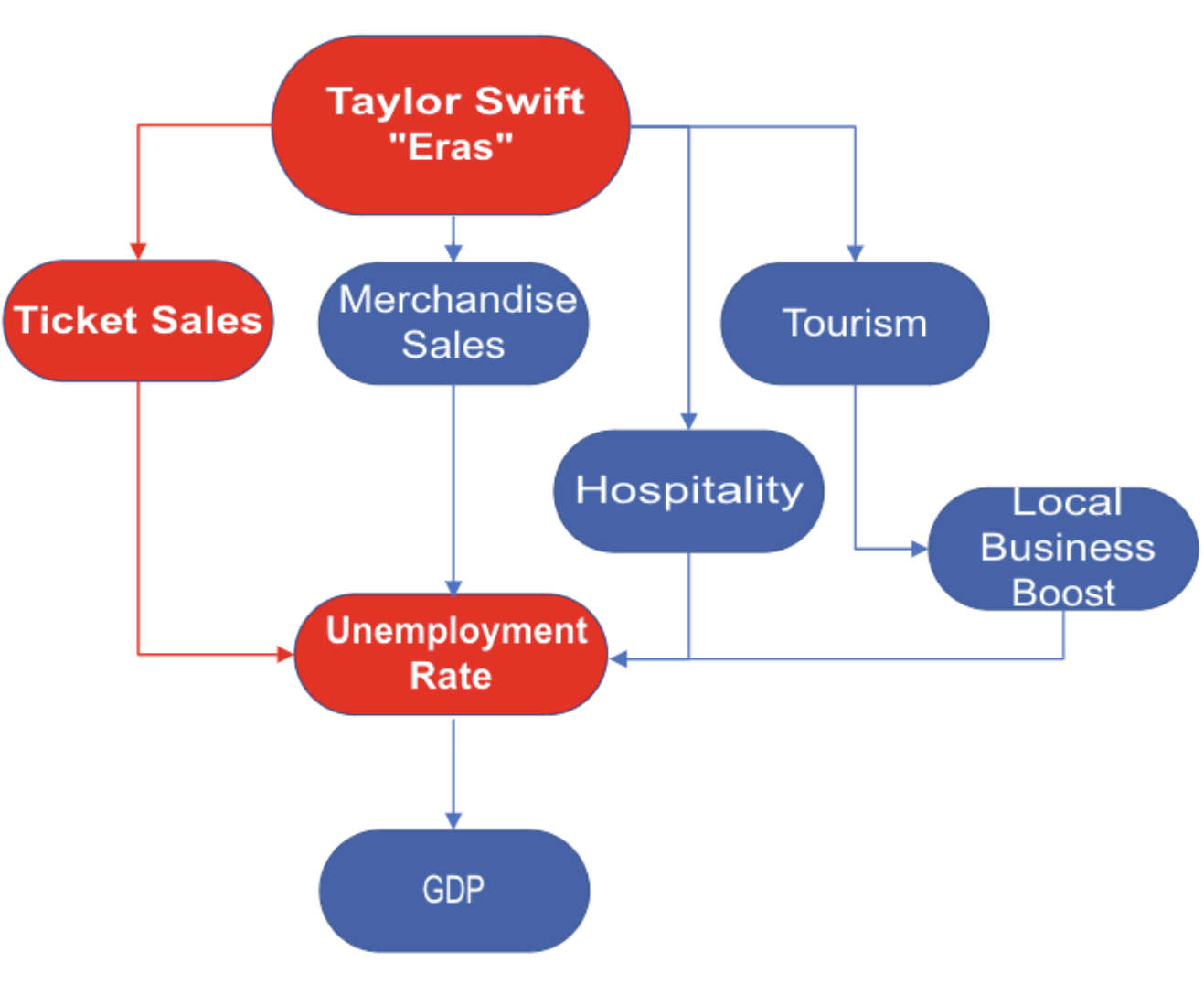
In this Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG), we illustrate the correlation between ticket sales and the unemployment rate. Unfortunately, we encountered challenges in obtaining precise ticket sales figures. As an alternative, we employed Google Trends, a widely-used tool, to measure the level of interest in both touring and non-touring cities. This approach allows us to infer potential concert attendance and discern variations in spending patterns across different cities. By leveraging Google Trends data, we aim to capture the essence of audience engagement and spending dynamics in lieu of explicit ticket sales figures.
__________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
DATA SOURCES


Our dataset is sourced from two primary channels: Google Trends and the Bureau of Labor Statistics. Google Trends provides an analytical platform for assessing the popularity of top searches in Google Search across diverse regions and languages. On the other hand, the Bureau of Labor Statistics, a division of the United States Department of Labor, serves as the authoritative source for our investigation into monthly unemployment rates. Combining insights from both platforms enables a comprehensive and multi-faceted analysis of the factors influencing our research.
Disclaimer: The data presented includes cities listed as MSAs, which stands for Metropolitan Statistical Areas. The choice to use MSAs arises from the fact that some cities where Taylor Swift performed did not individually appear on the Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) website, as the BLS reports unemployment rates by MSA. In such cases, we identified the MSA associated with the city or one that was in close proximity. For instance, Swift's performance in Arlington, TX is represented on our graph as DFW (Dallas-Fort Worth). This approach ensures a comprehensive representation of the economic context, incorporating both major cities and their surrounding metropolitan areas.
Note: To see block code, please see our master notebook or select "Show it" to view our work.
Run to view results
The table represents the tour dates for Taylor Swift's "The Eras Tour" in 2023. It includes key details such as the date of each event, the city where the event takes place, the venue hosting the performance, and the corresponding year. The tour spans various cities across the United States and includes iconic venues such as State Farm Stadium in Glendale, AZ, Allegiant Stadium in Las Vegas, NV, AT&T Stadium in Arlington, TX, and many more. The extensive list of tour dates showcases the widespread reach of Taylor Swift's performances throughout the year, offering fans across different regions the opportunity to experience her live music and captivating stage presence. The diversity of cities and venues reflects the scale and popularity of "The Eras Tour," making it a noteworthy and highly anticipated musical event in 2023.
Fun Fact! The opening night of Taylor Swift's The Eras Tour in Glendale, Arizona broke the record for the most-attended concert by a female artist in the US with 69,000 fans. The record was reportedly previously held by Madonna.
Run to view results
The provided data originates from Google Trends, utilizing the search term "taylor swift the eras tour" for the timeframe of 11/18/2022 to 11/18/2023. The chart is categorized into two groups: cities from Cincinnati to Las Vegas, where Taylor Swift performed, and cities from Salt Lake City to Reno, which were not tour locations. Additionally, Mexico City is included in the analysis due to its relevance as a tour location.
Two cities where Taylor Swift performed are not represented on the chart due to lower engagement levels. However, the majority of the U.S. tour cities are included based on the search criteria. The cities from Salt Lake City to Reno, where she did not perform, are part of the research to facilitate analysis on dummy cities. The relative scale, ranging from 0 to 100, serves as a metric to gauge engagement levels.
This data-driven approach aids in identifying cities with heightened excitement for Taylor Swift's tour, thereby offering valuable insights for potential ticket sales strategies within the Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG) framework. The inclusion of both tour and non-tour cities provides a comprehensive perspective for informed decision-making in relation to the tour's geographical impact.
Run to view results
In constructing our unemployment graph, we adopted a robust methodology by computing the three-month percent change for each city. Given that Taylor Swift's U.S. tour spanned from March to August, our analysis focused on a three-month window, capturing the month before and after her concert in each city. This approach allowed us to discern any discernible effects of her concerts on local unemployment rates.
Upon examining the data, we observed varying degrees of change in unemployment rates across different cities. Some cities, such as Cincinnati and DFW, demonstrated minimal fluctuations, while others, like Nashville and Chicago, experienced more pronounced shifts. It's important to note that these fluctuations may be attributable to diverse factors, prompting us to delve deeper into the analysis.
Of particular interest was the examination of cities where Taylor Swift did not perform. Strikingly, all the cities excluded from her tour exhibited increases in unemployment rates. This intriguing observation prompted further investigation to ascertain whether there was a discernible pattern or correlation between Taylor Swift's tour presence and the observed changes in local unemployment rates.
Important Note: The data point for Mexico City on our graph displays a 3-month percent change in unemployment of 16.53%. It's essential to recognize that Mexico City's data is on a distinct scale compared to the U.S. cities featured in our graph. Specifically, Mexico City represents unemployment rates in quarters of the year. To derive the 16.53% value, we considered the unemployment rates in Q1 and Q2 and calculated the overall change. It's crucial to highlight that this Mexico City data point will not be included in our regression graph. However, we wanted to explore how it would visually appear on the graph for informational purposes. As our analysis progresses, we will undertake a separate calculation to estimate the percent change in unemployment for Mexico City, Mexico, providing a more accurate representation aligned with our research framework.
__________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
ANALYSIS
When deciding how to run our analysis, we considered what regression most accurately reflected the relationship between our variables. In order to make our analysis more robust, we included non-touring cities. However, it is important that we controlled for a dummy variable in order to isolate the effect of local interest, and could illustrate the difference between cities where she did and did not stop.
The initial regression analysis undertaken exclusively isolates the impact of the variable of interest on the percentage change in unemployment. Notably, this analysis disregards the influence of the dummy variable, consequently providing insights solely into the correlation between local interest in Taylor Swift and fluctuations in the unemployment rate.
Run to view results
The regression output reveals a coefficient of -0.1068 for the variable "Interest." This indicates that with each 1-unit rise in Interest in Taylor Swift, there is a corresponding decrease of 0.1068 units in the Percent Change in Unemployment. It's important to observe that the R-squared value stands at a relatively low 0.016, suggesting a weak correlation. The accompanying graph visually depicts this relationship.
Run to view results
Subsequently, we conducted a regression analysis specifically depicting the impact of interest on the percentage change in unemployment, limited to cities included in the tour. It is noteworthy that, once again, the dummy variable is deliberately omitted from this particular analysis.
Run to view results
The regression output indicates a coefficient of 0.4005 for the variable "Interest," suggesting that with each 1-unit increase in Interest in Taylor Swift, there is a corresponding increase of 0.4005 units in the Percent Change in Unemployment specifically in touring cities. It is important to note the relatively modest R-squared value of 0.118, indicating a somewhat weak correlation. However, drawing a conclusive link between interest in Taylor Swift and an increase in the unemployment rate would be misleading, as this finding contradicts established knowledge. The accompanying graph visually represents this relationship for better clarity.
Run to view results
Run to view results
In our project, multiple regression analyses were conducted to assess various factors influencing the final prediction. The selected regression model incorporated a dummy variable indicating whether a city served as a tour stop. The model yielded an R-squared value of 0.238, signifying a moderate level of explanatory power. Notably, the coefficient associated with the variable of primary interest was smaller than its corresponding p-value, suggesting a limited impact on the unemployment rate.
Conversely, the tour stop dummy variable exhibited a substantial coefficient of 15.6, indicating a strong influence on unemployment. This observation underscores the significant differentiation in unemployment rates based on whether a Metropolitan Statistical Area (MSA) served as a tour stop, with a notable coefficient contrast of 15.6 compared to 0.012. The findings suggest that the presence of concerts in specific areas markedly contributes to variations in unemployment rates.
Run to view results
Presented here is the regression plot depicting our analysis of unemployment prediction in Mexico City. The plot exhibits distinct trend lines for non-touring cities and touring cities. Notably, non-touring cities display a negative correlation between the variable of interest and unemployment, whereas touring cities exhibit a positive correlation. This observed divergence could be attributed to various factors, such as population dynamics.
Introducing a compelling logistic regression analysis, this chart delves into the correlation between concert interest and our binary dummy variable signifying whether a city served as a tour stop. The title of the chart aptly encapsulates its core theme: "Logistic Regression: Tour Stop vs Local Concert Interest."
The significant coefficient of the dummy variable becomes evident through the starkly contrasting trend lines. This graphical representation underscores that cities with a higher level of interest in Taylor Swift experienced an increase in unemployment post-concert. However, it is essential to acknowledge that while correlation is evident, causation cannot be inferred directly. Therefore, the surge in unemployment following a concert does not necessarily imply that the demand for Taylor Swift is a direct cause of the observed increase in unemployment.
Run to view results
A noticeable negative correlation is observable in the distribution of data points on the plot. Significantly, tour stops tend to aggregate towards the lower end, whereas non-tour stops are predominantly situated towards the upper part of the chart. This observation implies that, as per the outcomes of this regression analysis, a plausible relationship exists between Taylor Swift's selection of tour locations and the corresponding local interest in her concerts.
The implications drawn from these findings suggest that in the process of selecting tour stops, Taylor Swift and her team potentially considered the local interest level, as evidenced by the discernible negative correlation. While the precise tools or methodologies utilized for this decision-making process are not explicitly outlined, it is conceivable that factors related to local interest played a role in shaping the overall tour itinerary. The chart introduces a noteworthy dimension to comprehending the strategic considerations that may have influenced the selection of tour locations.
Run to view results
Based on our regression analysis, we estimated that Mexico City, with an interest level of 79, would experience a 9.59% increase in the unemployment rate in the month following the concert, positioning it at the corresponding point on the graph (refer to the point on the last slide). Interestingly, this predicted increase is lower than the actual percent change in the unemployment rate for Mexico City during that time frame, which recorded a 16.53% surge.
The discrepancy between our prediction and the actual outcome prompts further investigation. One plausible explanation is the presence of unaccounted factors that could have influenced the observed increase in unemployment. For efficiency and simplicity, our project did not incorporate certain variables, acknowledging the complexity of including all relevant factors.
Seasonal variations, particularly the summer timing of the concert in U.S. cities used as data points, could contribute to the observed discrepancies. Additionally, the broader context of the U.S. experiencing an overall increase in unemployment during the same period, attributed by economists to factors such as an aging population and the subsequent expansion of the labor force, may have played a role.
It is worth noting that a more thorough examination, including these additional factors and potentially refining the predictive model with enhanced Python proficiency, could lead to a more accurate and comprehensive regression analysis. Despite the current limitations, this insight underscores the importance of considering various contextual elements to refine predictions and draw more nuanced conclusions about the impact of events on economic indicators.
__________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
ENCORE
In the world of music, where art meets economics, the impact of global sensations like Taylor Swift reverberates far beyond the melodies and lyrics. As we delved into the economic tapestry woven by Taylor Swift's "The Eras Tour" in Mexico, our journey unfolded a nuanced narrative, blending data-driven analysis with the artistic aura that Swift casts upon her audiences.
Our endeavor began with the grandeur of Taylor Swift's musical legacy, spanning from country roads to pop anthems, creating a formidable presence in the music industry. As "The Eras Tour" embarked on its international journey, we set out to unravel the economic impact it would wield on the Mexican economy, employing a multifaceted approach rooted in regression analyses and a Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG).
Our Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG) served as a visual compass, guiding us through the intricate relationships between variables influenced by the tour. From ticket sales and merchandise to hospitality and tourism, we navigated the ripple effects that resonate across industries, ultimately shaping the unemployment rate—a keystone indicator in the economic symphony.
However, the scarcity of recent, authoritative data led us to navigate alternative methodologies, embracing adaptability to extract valuable insights. The Google Trends data became our compass, gauging audience engagement in lieu of explicit ticket sales figures. This creative pivot, while acknowledging its limitations, allowed us to contribute to a nuanced understanding of the tour's economic impact.
Our regression analyses conducted on U.S. cities revealed intriguing correlations. The correlation between local interest, represented by Google Trends data, and the percentage change in unemployment unfolded a narrative suggesting a potential influence of concert presence on unemployment rates. Yet, the complexity of these relationships was further illuminated when considering whether a city served as a tour stop, highlighting substantial differentiation in unemployment rates.
A logistic regression analysis painted a vivid picture, hinting at a strategic alignment between tour locations and local interest levels. While correlation was evident, causation remained elusive—Taylor Swift's concerts might be correlated with increases in unemployment, but we tread cautiously in attributing causation to this relationship.
As our analysis focused on Mexico City, the estimated 9.95% increase in the unemployment rate stood in stark contrast to the actual 16.53% surge observed. The discrepancy prompted introspection, acknowledging unaccounted factors and the complexity of economic dynamics. Seasonal variations, the broader U.S. economic context, and the absence of certain variables showcased the intricacies involved in predicting economic outcomes.
In the symphony of Taylor Swift's "The Eras Tour," our journey showcased the interconnected melodies of art and economics. From the thrill of record-breaking concerts to the economic nuances shaping local landscapes, the tour's impact extended beyond the confines of the stage. Our analysis, though a snapshot in time, underscores the importance of considering diverse factors and refining predictive models to truly capture the economic resonance of cultural phenomena.
As Taylor Swift continues to command stages worldwide, her musical odyssey leaves an indelible mark not only on hearts but on the economic landscapes she traverses. In the grand orchestration of "The Eras Tour," the final notes linger, inviting economists and enthusiasts alike to anticipate the next chapter in the ever-evolving interplay between music and prosperity.
