Do heroin metabolites appear in solid drug samples?
Objective
To determine how common it is for 6-MAM and 3-MAM to appear in solid street drug samples. The motivation is that 6-MAM and 3-MAM are considered downstream biological/physiological metabolites used to identify exposure to heroin in post-mortem toxicology. In the human body, heroin is metabolized to 6-MAM (and then to morphine).
Analysis was conducted on June 20, 2024 to answer an internal team question about classification of polysubstance overdose deaths.
Summary of Findings
6-MAM (and much less frequently 3-MAM) were found in 413 samples; by comparison there were 875 heroin samples. 46% of heroin samples also contained 6-MAM, but in n=9 samples 6-MAM was found without heroin present. Acetylcodeine was the next most commonly found substance in samples containing 6-MAM.
By geography, 6-MAM was mostly commonly found in heroin in TX (93%), CA, AZ in the top tier, followed by WA and OR (63%). The following tier was NC (43%), MI (35%), and NY (35%).
Of samples containing 6-MAM, the form was black tar heroin for 33% (all heroin samples), going up to 45% (6-MAM in primary abundance only).
Solid drug samples routinely contain 6-MAM. In 9/413 samples, 6-MAM was found without heroin.
Alternate hypothesis considered
We also wanted to know if detection of 6-MAM could be an artifact of the GCMS-based detection method. Upon consulting with our analytical chemist, we believe that 6-MAM was present in the original samples because there are many heroin samples without 6-MAM and because the abundance of 6-MAM varies by sample; typical GC breakdown products appear consistently along with the parent molecule, and tend to be detected in consistent proportional abundance.
Semantic clarification
The word metabolite used in post-mortem toxicology (or urine analysis) is used to indicate a molecule that has been altered from a parent substance due to physiological processes (e.g., metabolism in the human body) often by enzymatic action. In analytical and synthetic chemistry, the word metabolite is used more broadly to indicate downstream products generated by chemical processes. While similar in concept, we refer to metabolite in the first sense because of the context of our research motivation regarding post-mortem toxicology.
Methods
We obtain drug samples from 140+ harm reduction programs, clinics, hospitals, EMS, health departments, and drug user unions in 35 US states, covering about 200 counties. Samples are donated voluntarily, and collected anonymously. Mailed-in samples are analyzed using exactive (high resolution) GCMS, with untargeted search, and pure standard verification of identified substances. See laboratory methods and codebook and GitHub repo for code and dataset, and further details.
🏷️ Two data caveats: We get more more samples from NC, WA, NY, CA, and MI than other states. Geographic data below should not be construed as prevalence. And people may preferentially send us samples because they caused unusual reactions. There is no possible data source on street drugs that is fully generalizable. Got it? Okay!
Results
All Sample origins
How many solid drug samples with heroin metabolites have been detected?
Was 3-MAM always found with 6-MAM?
Yes, 3-MAM was always found with 6-MAM. There are 12 samples with 3-MAM, and all of them also contain 6-MAM.
What percent of heroin samples contained 6-mam?
What else was found with 6-MAM and 3-MAM?
Were there any samples that contained 6-MAM or 3-MAM that didn't also contain heroin?
For samples containing 6-MAM and 3-MAM, what were the collection methods?
We want to get a sense if these samples were collected as powder (scoop) versus residue from pipes/syringes to reduce the chance of cross-contamination influencing our inference.
About half the samples were spatula which gives us more confidence in the findings. But surprising to see 2 pills containing the heroin metabolites! Let's look into that.
Fake pills with heroin metabolites?
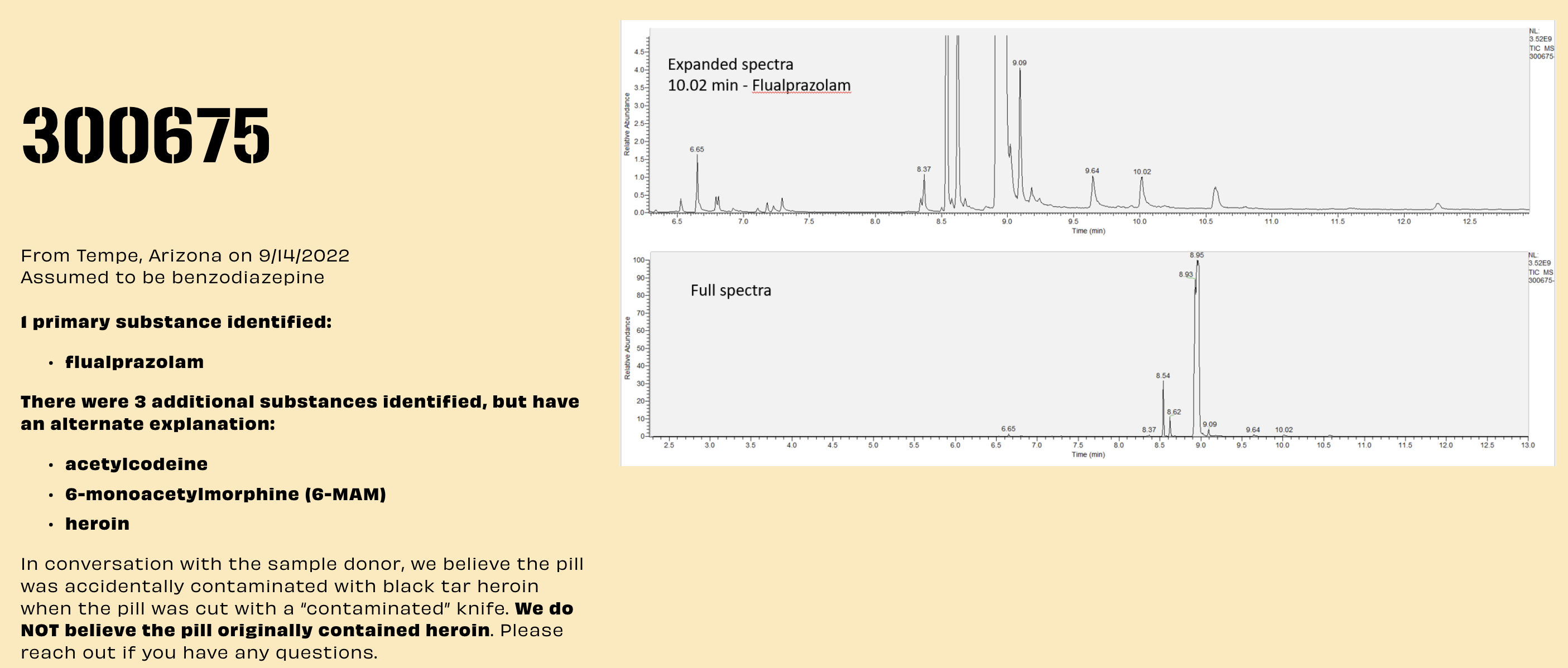
Sample 300675 was contamination of a fake flualprazolam pill.

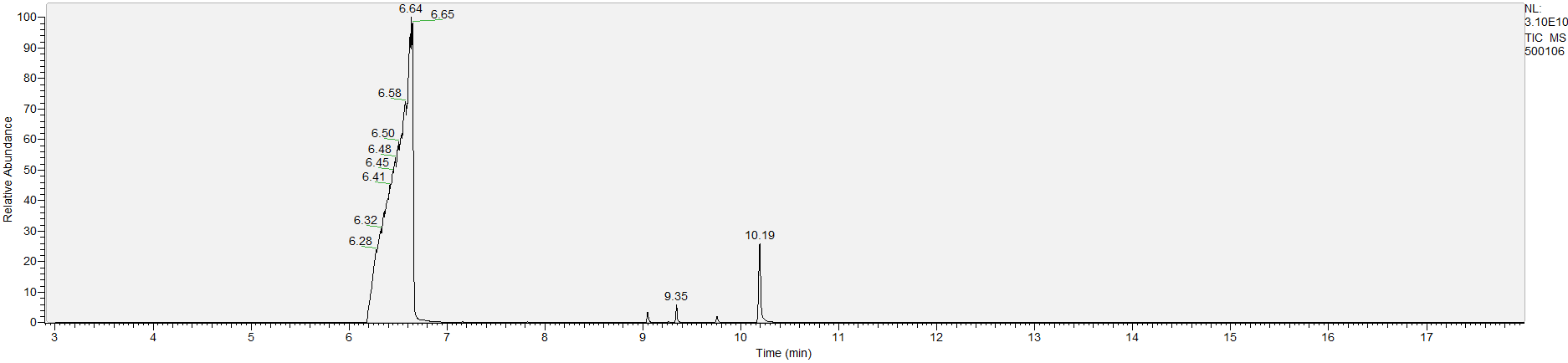
Major substances in graph: Peak 10.19 = fentanyl Peak 6.64 = acetaminophen Peak 9.35 = 6-monoacetylmorphine (6-MAM)
Looking at the chromatogram, 6-MAM was in relatively less abundance, similar to heroin and acetylcodeine. The designation of trace vs. primary abundance is <5% peak height area of the primary detected substance (relative abundance on vertical axis). So, it is worth looking into how much of the 6-MAM and 3-MAM was detected by abundance.
What was the relative abundance of heroin metabolites?
6-MAM and 3-MAM concentrations are in primary abundance in about ⅓ of samples that contain them.
Where are heroin metabolites found in the US?
So it looks like 6-MAM may show up more in areas where black tar heroin is present. Some states had few samples, limiting inference.
What type of heroin (tar or powder) is 6-MAM found in?
Let's look at it first with all 6-MAM samples.
Now let's look by where 6-MAM is only in primary abundance.
So it appears that 6-MAM shows up in primary abundance in both powder and tar samples.